What is digital public infrastructure (DPI)?
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) is a digital network that enables countries to safely and efficiently deliver economic opportunities and social services to all residents. DPI can be compared to roads, which form a physical network that connects people and provides access to a huge range of goods and services.
DPI allows people to open bank accounts and receive wages faster and more easily. It allows governments to support citizens more quickly and efficiently, especially during emergencies. And it enables entrepreneurs to reach customers far and wide.
ALSO READ | What is Linux? A Comprehensive Guide
India, through India Stack, became the first country to develop all three foundational DPIs, Digital identity (Aadhar), Real-time fast payment (UPI) and Account Aggregator built on the Data Empowerment Protection Architecture (DEPA).
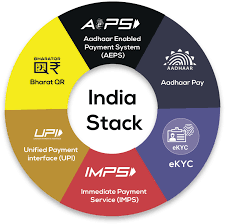
What are the Pillars of India’s DPI Ecosystem?
- Aadhaar:
- Aadhaar is a strategic policy tool for social and financial inclusion, public sector delivery reforms, managing fiscal budgets, increasing convenience and promoting hassle-free people-centric governance.
- DigiYatra:
- DigiYatra is a Biometric Enabled Seamless Travel (BEST) experience based on a Facial Recognition System (FRS).
- Air passenger traffic in India was estimated to be over 188 million in airports across India in the financial year 2022, out of whom over 22 million were international passengers.
- DigiYatra is a Biometric Enabled Seamless Travel (BEST) experience based on a Facial Recognition System (FRS).
- DigiLocker:
- DigiLocker has 150 million users, six billion stored documents, and done with a tiny budget of RS 50 crore over 7 years.
- The users can store their documents such as insurance, medical reports, PAN card, passport, marriage certificate, school certificate etc.
- UPI:
- UPI (Unified Payment Interface) has crossed eight billion transactions per month and transacts a value of USD 180 billion a month, or about a staggering 65% of India’s GDP per annum.
- UPI is currently the biggest among the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) operated systems including National Automated Clearing House (NACH), Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), Aadhaar enabled Payment System (AePS), Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS), RuPay etc.
Other DPI Initiatives:
- Aadhaar-Enabled Services: Numerous govt services, including subsidies, welfare programs, and digital lockers, are linked to Aadhaar for authentication & efficient delivery.
- Digital India: To transform India into a digitally empowered society. It encompasses diverse initiatives related to digital infrastructure, connectivity, e-governance, and digital literacy.
- BharatNet: The BharatNet initiative strives to provide broadband connectivity to rural and remote areas.
- e-Government Services: India has made substantial strides in offering a wide array of government services online.
- Digital Health Initiatives: National Digital Health Mission (NDHM)The NDHM endeavors to create a comprehensive digital health ecosystem, incorporating health records, telemedicine services, and health ID cards.
Conclusion:
In summary, India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) comprises essential components such as digital identification, payment infrastructure, data exchange solutions, and government-prescribed frameworks like DEPA. Alongside these core elements, various initiatives and programs collectively contribute to India’s digital transformation, promoting accessibility, efficiency, and inclusivity in public services and governance. The government’s ongoing investments in these digital infrastructure projects signify its commitment to driving digital progress throughout the nation.